Presentation
ACMP07 - High Performance Computing Derived Biological Multiplex Network Uncovers Distinct Pathways Underlying Opioid and Nicotine Addiction
Presenter
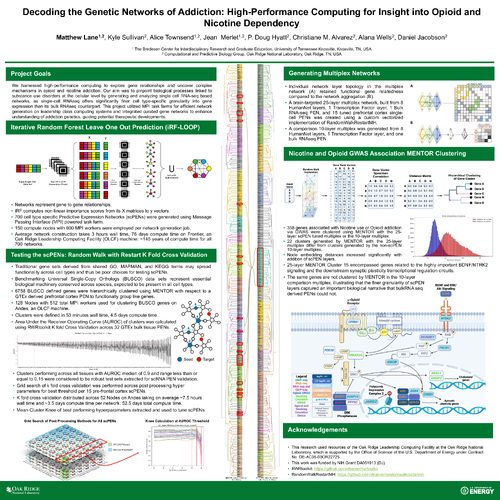
DescriptionLeveraging High-Performance Computing (HPC) for biological network generation, key insights into the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms supporting opioid and nicotine addition have been uncovered. Using distributed network generation software on the Frontier supercomputer, the authors processed 700 single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) data sets to construct biologically robust multiplex networks. By employing an MPI task farm as a scheduling method, the network generation software computed networks in 3 real-time hours compared to the average 76 day CPU-time, using iterative Random Forest (iRF) Leave One Out Prediction (LOOP). Network layers were validated using RWR with k Fold cross validation against independently curated GO terms and clustered using MENTOR, an algorithm developed for the clustering and visualization of RWR rank order embeddings. The findings highlight transcriptional regulation via transcription factors and epigenetic mechanisms implicated in neural development. This research not only illuminates our current understanding of nicotine and opioid addiction, but also demonstrates the importance of HPC network generation and validation techniques.
TimeTuesday, June 410:07 - 10:08 CEST
LocationHG F 30 Audi Max
Session Chair
Event Type
Poster